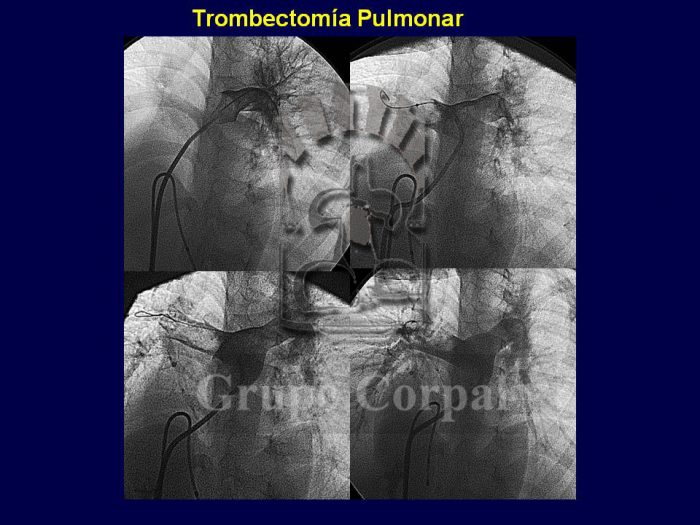
Clot formation in the venous system is common in people with reduced mobility or bed rest, and in patients who undergo surgery, largely for trauma processes. These silent venous clots, or thrombi, can lead to acute pulmonary embolism, a serious condition capable of causing chest pain, sudden onset dyspnoea and intense systemic desaturation. Massive acute pulmonary embolism can be fatal. If it becomes chronic, it can cause pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure. Besides prevention in prone patients, only urgent surgery or systemic fibrinolysis can be considered active attitudes. Its diagnosis is based on suspicious clinical symptoms, confirmed by an urgent CT scan with contrast. The sooner the diagnosis, the sooner therapy can be contemplated. Time is golden in this condition.
In our hospital we have a system for the aspiration of clots located in the lung by urgent cardiac catheterisation in the initial phase. A cannula is inserted up to the central pulmonary artery, through which catheter is passed to fragment and aspirate the thrombus. This can be combined with fibrinolysis “in situ”, favouring the lysis of the residual thrombus. Thrombectomy has saved lives and is very effective when the clot is still fresh. The combination of fragmentation, aspiration and lysis of the thrombus revascularises the affected lung, restores oxygenation and prevents heart failure and pulmonary hypertension.